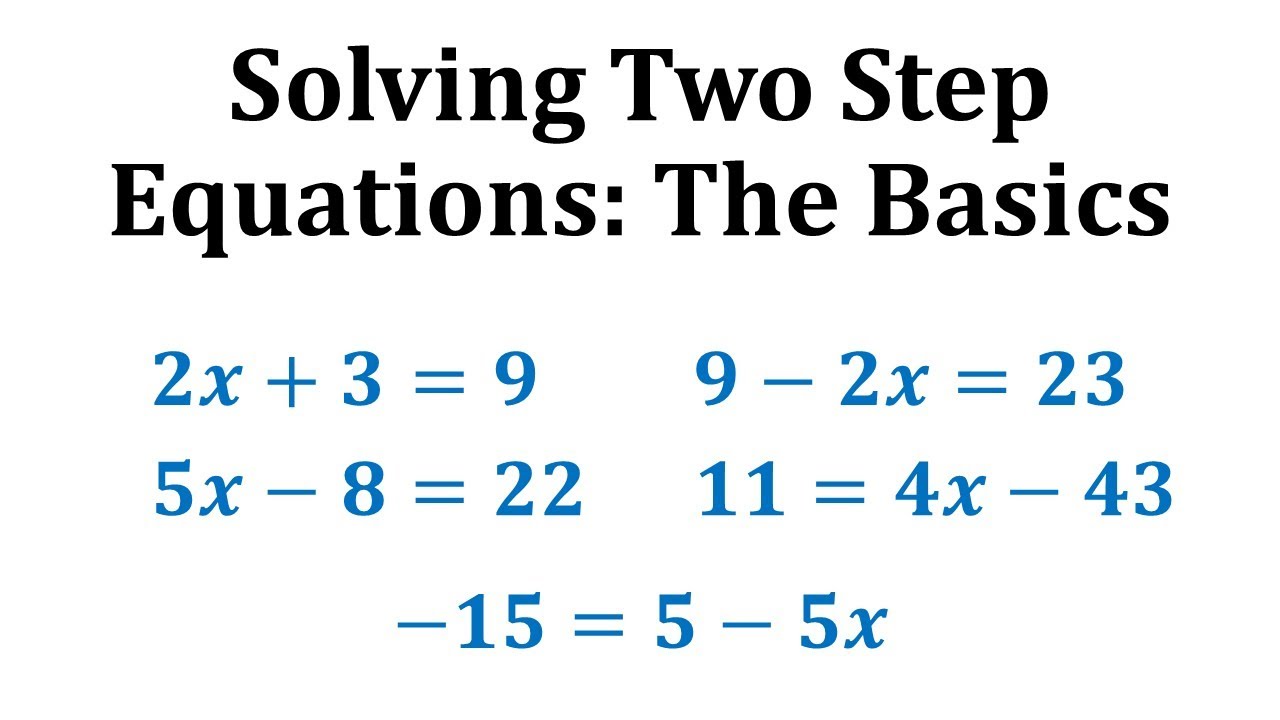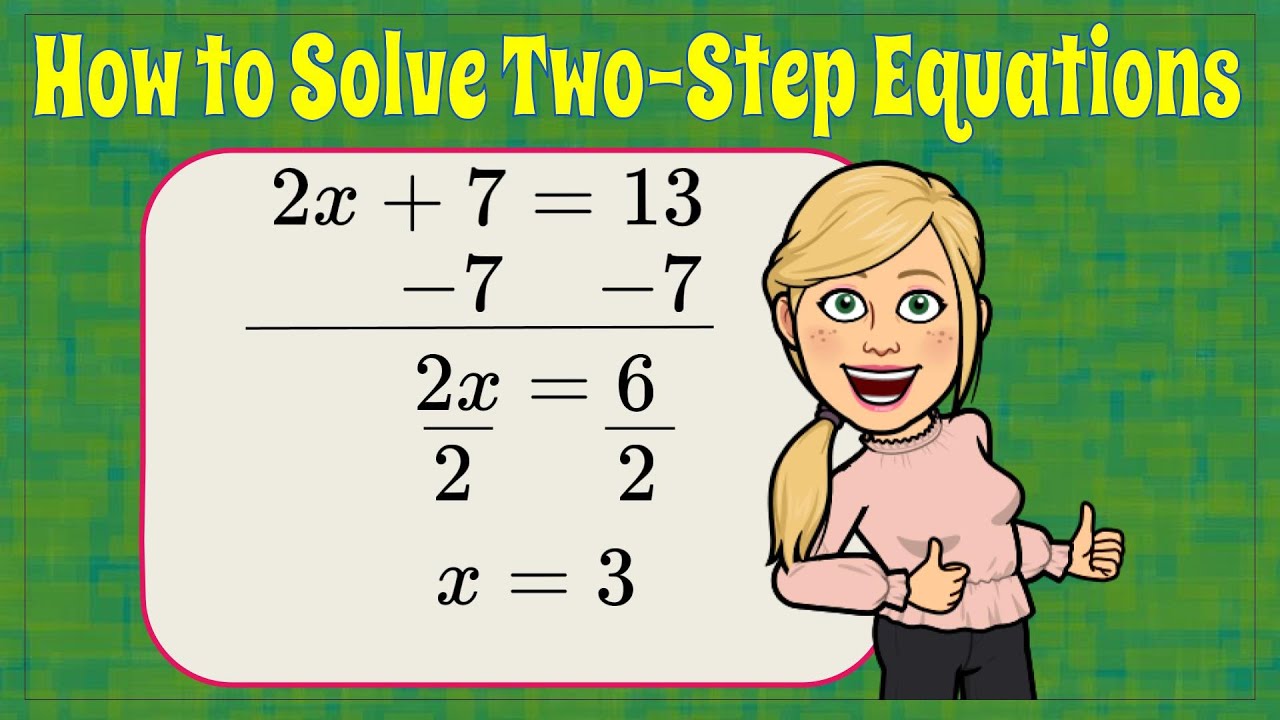Effective Ways to Solve Two-Step Equations for Better Results in 2025
Solving two-step equations is an essential skill in algebra that helps students understand mathematical concepts and improves their problem-solving abilities. This article will explore various strategies and tips for effectively solving two-step equations, including examples, practice problems, and common mistakes to avoid. Whether you’re a student looking to enhance your mathematical skills or a teacher seeking educational resources for math, this comprehensive guide offers valuable insights.
Understanding Two-Step Equations
Two-step equations refer to algebraic expressions that require two operations to isolate the variable. These can range from simple two-step equations, such as \(2x + 3 = 7\), to more complex variants with fractions or decimals. Understanding two-step equations begins with recognizing the steps to solve two-step equations: performing the inverse operations and isolating the variable step-by-step. By mastering these fundamentals, learners can tackle mathematical equations with confidence, whether dealing with basic algebra problems or more systematic learning of algebra.
Steps to Solve Two-Step Equations
To solve a two-step equation, follow these sequential steps:
- Identify the equation: Start with the given equation (for example, \(3x + 4 = 10\)).
- Isolate the variable: Subtract 4 from both sides to eliminate the constant (resulting equation: \(3x = 6\)).
- Solve for the variable: Divide both sides by 3 to find \(x = 2\).
These steps to solve two-step equations work effectively for various case studies, including those involving zero or negative numbers. Solving for x in equations through this structured approach helps ensure learners grasp essential equation-solving techniques.
Common Mistakes in Two-Step Equations
Students often make mistakes when solving two-step equations, such as:
- Forgetting to apply inverse operations correctly.
- Making arithmetic errors while calculating.
- Confusing the order of operations (PEMDAS: Parentheses, Exponents, Multiplication and Division, Addition and Subtraction).
- Neglecting to check their answers by substituting back into the original equation.
Avoiding these common pitfalls is crucial to mastering algebraic expressions, thus enhancing overall algebra skills. Recognizing where students typically struggle can also allow educators to focus their teaching more effectively.
Two-Step Equation Examples
Here are some simple two-step equations and their solutions:
- **Example 1:** \(5x – 7 = 18\)
- Add 7 to both sides: \(5x = 25\)
- Divide by 5: \(x = 5\)
- **Example 2:** \(3x + 2.5 = 11\)
- Subtract 2.5 from both sides: \(3x = 8.5\)
- Divide by 3: \(x = 2.833\) (or \(\frac{17}{6}\))
Practicing various two-step equations provides a solid foundation in algebra, allowing students to appreciate the logic behind the calculations, from simple variables in equations to more abstract mathematical concepts.
Tips for Solving Two-Step Equations
Mastering two-step equations can be achieved through multiple practices and advanced strategies. Here are some top tips for students striving to understand algebra better:
Equation Solving Techniques
Adopting effective equation-solving techniques can significantly improve performance. Emphasize the importance of:
- Using clear notation and methodical approaches for each part of the solution.
- Regular practice with two-step equations worksheets that encompass a variety of equation types, including those with fractions and decimals.
- Learning two-step equations through interactive means, whether through educational videos or engaging math games for learning.
By reinforcing these techniques, students can confidently progress from simple two-step equations to more complex algebraic challenges.
Two-Step Equations Practice
Consistency is key to mastering two-step equations. Set aside practice time focusing on various equation problems. Use resources such as:
- Two-step equation practice worksheets available online.
- Math study guides covering essential concepts in algebra.
- Structured quizzes that reinforce the learning outcomes of solving for variables effectively.
This consistent practice cultivates a deeper understanding of algebra and encourages productive problem-solving methods.
Using Tools and Resources
There are various tools available for learners that can aid in their understanding of two-step equations. Practical resources include:
- Two-step equation calculators that simplify the solving process.
- Online educational platforms that offer structured lessons in algebra.
- Interactive algebra tutorials that provide feedback and adjust learning to the user’s pace, addressing individual learning needs.
Utilizing these tools enhances comprehension and confidence among students, making complex algebra concepts more accessible and manageable.
Two-Step Equations with Fractions and Decimals
Two-step equations with fractions or decimals may appear challenging at first glance, but understanding their operation can significantly ease the solving process. Here’s how to approach these:
Working with Fractions
When working with two-step equations containing fractions, the focus may shift to eliminating the fraction first. Consider the equation \( \frac{1}{2}x + 3 = 5\). The preferred approach is to multiply through by the denominator:
- Multiply the entire equation by 2: \(x + 6 = 10\).
- Subtract 6 from both sides: \(x = 4\).
Emphasizing the elimination of fractions streamlines the process, paving the way for successful problem-solving in mathematical concepts related to fractions.
Handling Decimals
For two-step equations with decimals, adapt the solving strategy while maintaining consistency with previous methods. Take, for example, the equation \(2.5x – 1.2 = 4.8\).
- Add 1.2 to both sides: \(2.5x = 6\).
- Divide by 2.5: \(x = 2.4\).
Addressing the challenges posed by decimals and fractions in two-step equations provides students ample practice to enhance their algebraic comprehension.
Real-World Applications of Two-Step Equations
Understanding two-step equations goes beyond academic contexts; they present a critical part of real-world problem-solving scenarios. From financial planning (calculating loans) to physics (unit conversions), the aptitude for solving variables in equations translates into practical applications. Examples may include:
- Budgeting monthly expenses: e.g. saving money with variable costs.
- Understanding speed and distance problems in physics: e.g. \(distance = speed \times time\).
- Utilizing two-step equations in competitive contexts: sports strategies based on statistics.
Highlighting how equation solving is intertwined with real-life challenges reinforces the value of mastering these skills.
Key Takeaways
- Solving two-step equations involves sequential operations to isolate variables.
- Practice through worksheets, games, and educational resources can enhance understanding.
- Common mistakes can be avoided by fostering skills such as problem-solving techniques and personal education methods.
- Working with fractions and decimals includes unique strategies to simplify problem-solving.
- Real-world applications underline the importance of mastering algebraic skills.
FAQ
1. What are simple two-step equations?
Simple two-step equations refer to algebraic expressions that require two operations for solution completion, usually involving the isolation of a variable using simple arithmetic. Examples include equations like \(2x + 3 = 7\) where straightforward inverse operations result in the value of \(x\).
2. How can I practice solving two-step equations effectively?
Using resources like online algebra practice tests, math homework help websites, and interactive educational videos are effective ways to practice two-step equations. Repeated exposure to various equation types enhances understanding and promotes confidence in problem-solving skills.
3. What are common errors made when solving linear equations?
Common errors include misapplying inverse operations, failing to combine like terms, or arithmetic errors arising from careless calculations. Additionally, not checking answers by substituting them back into the original equation can also lead to unnoticed mistakes.
4. Are there any educational resources specifically for learning two-step equations?
Yes, many educational platforms offer resources tailored to help with understanding two-step equations, including interactive math websites, algebra tutorials, and practice problem worksheets that cater to different learning styles and levels.
5. What tips can I use to improve my equation solving techniques?
To improve solving techniques, focus on double-checking your steps, working through problems methodically, and using visual aids to map out your thought process. Regular practice will also clarify concepts, minimizing common mistakes in two-step equations.
6. How do two-step inequalities differ from equations?
Two-step inequalities involve a similar process as two-step equations, but they differ in that the solution may involve a range of values rather than a single solution. The key is understanding how to work with the inequality symbols (e.g., ) while applying the same inverse operation principles.
7. Where can I find two-step equation calculators?
Two-step equation calculators can be found on educational math websites and through mathematical software applications, many of which allow users to input equations and receive step-by-step solutions, serving as effective learning aids for algebra.