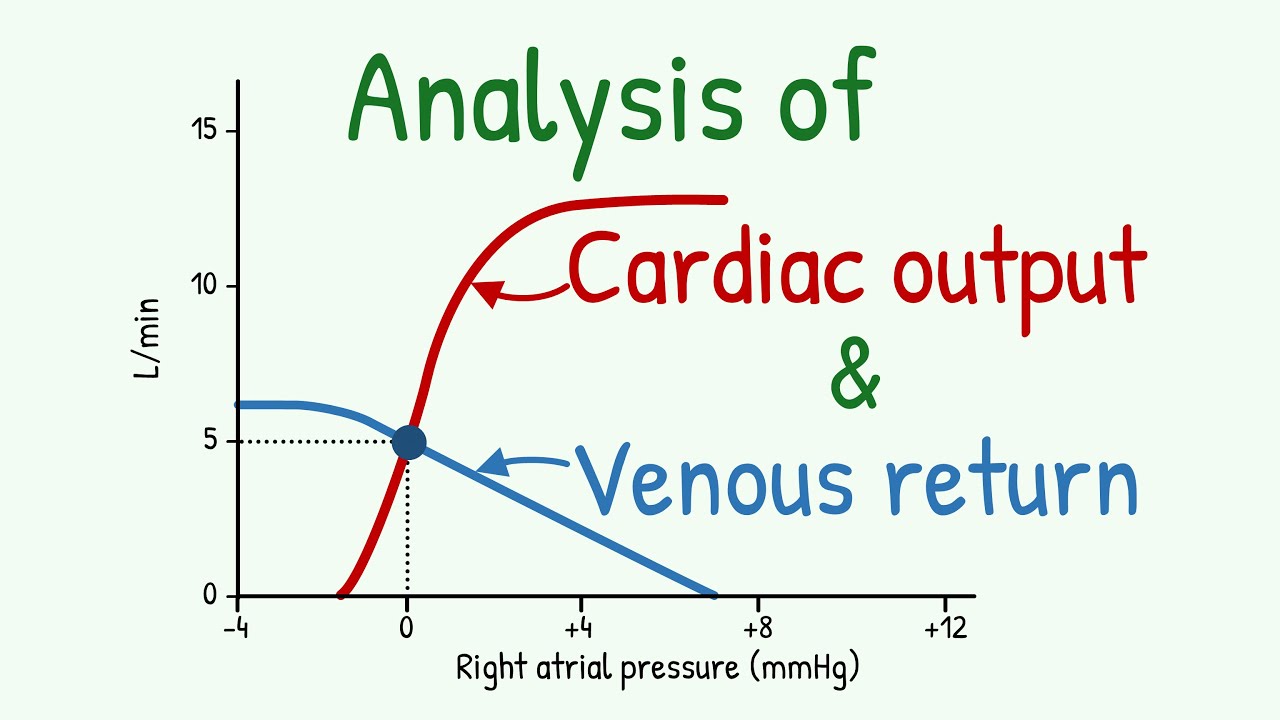
Effective Ways to Calculate Cardiac Output: A Complete Guide for 2025
Understanding how to calculate cardiac output (CO) is fundamental for assessing the health of the cardiovascular system. Cardiac output reflects the volume of blood the heart pumps per minute and is pivotal in evaluating cardiac function, especially in patients with heart disease or during physical exertion. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore various methods for CO calculation, their clinical significance, and how they enhance heart disease management.
Understanding Cardiac Output and Its Importance
Cardiac output is a crucial physiological parameter that indicates the efficiency of the heart’s pumping ability. It is determined by two primary factors: stroke volume and heart rate. Stroke volume is the amount of blood ejected by the heart with each contraction, while the heart rate refers to the number of beats per minute. Together, these components provide insights into the heart’s performance under various physiological conditions.
The Cardiac Output Formula
The simplest and most common formula to calculate cardiac output is:
CO = Stroke Volume x Heart Rate
For instance, if a patient has a stroke volume of 70 mL and a heart rate of 75 beats per minute, the cardiac output would be 5,250 mL/min (or 5.25 L/min). This formula serves as the basis for several methods of cardiac output measurement, further highlighting the importance of accurate stroke volume and heart rate assessment in understanding a patient’s cardiovascular dynamics.
Components Influencing Cardiac Output
Several factors influence cardiac output, including blood pressure, venous return, and cardiac contractility. Healthy heart function typically maintains a normal cardiac output range, but conditions such as heart failure or significant blood loss can decrease stroke volume, thereby reducing overall CO. Factors like myocardial oxygen demand and metabolic rate play significant roles in affecting how well the heart delivers blood throughout the body.
Key Techniques for Measuring Cardiac Output
Various methods exist to measure cardiac output, including:
– **Invasive monitoring**, such as cardiac catheterization
– **Thermodilution methods** typically used in critical care environments
– **Echocardiography**, which leverages ultrasound technology for non-invasive measurement
Each technique has its benefits and drawbacks, influenced by the clinical setting, patient condition, and required precision level. Awareness of these methods enhances practitioners’ ability to optimize patient care through tailored cardiovascular assessments.
Advanced Techniques for Accurate Cardiac Output Measurement
While traditional methods are invaluable, newer and advanced techniques provide enhanced accuracy in assessing cardiac output, allowing more intricate clinical assessments.
The Fick Principle
The Fick principle states that the amount of a substance consumed or produced by the body equals the total blood flow times the difference of that substance’s concentration between arterial and venous blood. This principle enables accurate measurements of oxygen consumption and is particularly applicable in calculating cardiac output. By directly measuring oxygen uptake and using hemoglobin levels, technicians can deduce the CO with a detailed understanding of the body’s metabolic demands, thus providing indispensable information for heart disease management.
Echocardiography Variable Analysis
Echocardiography is a widely used non-invasive method to assess cardiac output. By visualizing heart structures in real time via ultrasound, healthcare providers can calculate stroke volume by considering the dimensions of the left ventricle and the flow velocity through the aortic valve. For optimal results, practitioners should familiarize themselves with echocardiogram interpretation and practice standardization to ensure consistent data collection during evaluations.
Automated Methods and Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies, including novel automated methods for cardiac output monitoring, promise future developments in practice. These tools facilitate continuous monitoring of cardiac function and improved patient outcomes through personalized CO management protocols. Advanced telemetry monitoring systems can automate data collection and provide instant feedback on cardiac performance, which is essential for high-risk patients.
Cardiac Output in Clinical Practice: Implications and Applications
Regular monitoring and correct assessment of cardiac output are critical for effective management of heart diseases and overall cardiovascular health.
Relevance of Cardiac Output in Heart Disease Management
In patients with conditions like coronary artery disease or heart failure, accurate knowledge of cardiac output is essential for treatment planning and assessment of therapy effectiveness. A lower-than-normal cardiac output can indicate the need for intensified therapies, possibly involving medications that improve cardiac contractility or inotropic support. Understanding individual cardiac output can lead to tailored treatment strategies that improve overall outcomes and quality of life for patients with diseased hearts.
Exercise Physiology and Cardiac Function
Cardiac output plays a vital role in managing sports performance and exercise conditioning. During physical activity, the heart’s output must significantly increase to accommodate the demands of active muscles for oxygen and nutrients. Understanding how cardiovascular dynamics change during exercise can help athletes optimize performance and potentially prevent sports-related injuries by ensuring appropriate monitoring of their heart responses.
Fluid Balance and Cardiac Output
Fluid therapy also relies heavily on a precise understanding of cardiac output. Patients with hypovolemia or sepsis often exhibit changes in fluid distribution and hemodynamics, necessitating accurate CO assessments to guide interventions. Strategies involving volume load and pressure load must consider the current cardiac output to optimize therapy and outcomes.
Key Takeaways
- Cardiac output is essential for assessing heart efficiency and health.
- Techniques such as echocardiography and the Fick principle provide diverse methods for accurate measurements.
- Monitoring cardiac output can improve outcomes in heart disease management.
- Understanding CO in exercise physiology aids in performance and injury prevention.
- Effective fluid management requires careful consideration of cardiac output.
FAQ
1. What are the normal ranges for cardiac output?
The typical cardiac output normal range for an individual at rest is between 4 to 8 liters per minute, depending on various factors like fitness level, age, and overall cardiovascular health. Understanding these metrics helps healthcare professionals determine the adequacy of a patient’s circulatory efficiency.
2. How does heart rate affect cardiac output?
Heart rate plays a crucial role in determining overall cardiac performance. An increase in heart rate can enhance cardiac output unless stroke volume declines simultaneously. Conversely, a lower heart rate may reduce cardiac output, particularly if stroke volume remains relatively constant; thus, maintaining a balanced heart rate is essential for optimal cardiovascular health.
3. What impact does exercise have on cardiac output?
Exercise physiology significantly increases myocardial demand, leading to higher cardiac output to sustain physical activities. Regular exercise can enhance the heart’s ability to increase output efficiently during high-intensity efforts, promoting better cardiovascular conditioning and overall health.
4. How does one measure stroke volume accurately?
Stroke volume measurement can be achieved through several means, such as echocardiography or thermodilution techniques. Practitioners should select a method based on clinical need and setting to ensure precision in assessing this critical component impacting cardiac output.
5. What role does cardiac output play in heart failure?
In cases of heart failure, monitoring cardiac output becomes crucial for treatment. Lowered cardiac output may necessitate changes in medication, therapy adjustments, and patient management strategies to optimize overall cardiac health.
6. Can cardiac output be affected by hydration levels?
Yes, fluid balance significantly influences cardiac output. Dehydration can reduce blood volume, leading to a diminished cardiac output, while proper hydration supports optimal circulation and cardiac function.
7. Are there any software tools available for cardiac analysis?
Yes, emerging software tools for cardiac analysis assist clinicians in evaluating various cardiovascular metrics, including detailed monitoring of cardiac output. These applications can facilitate remote patient monitoring and provide personalized insights into an individual’s cardiac health.