How to Properly Calculate Error: Essential Methods for 2025 Success
In various fields such as statistics, science, finance, and engineering, understanding how to **calculate error** is crucial. Accurately determining the level of error in data collection or experiments helps ensure that results are credible and reliable. This article will explore essential methods for calculating error and their importance for success in 2025. We will discuss the types of errors, standard error calculation methods, and practical applications to help you enhance your decision-making processes.
Understanding Types of Errors
Before diving into specific calculation methods, it’s vital to understand the different types of errors that can occur. Errors can be broadly classified into two categories: **systematic error** and **random error**. Systematic errors are consistent, repeatable errors associated with faulty equipment or biased procedures. On the other hand, random errors are unforeseen variations that happen due to unpredictable factors. Recognizing these types of errors allows you to select the most appropriate **error calculation method** for your needs.
Systematic Errors and Their Implications
Systematic errors can significantly impact the reliability of measurements and results. For example, if a balance scale is improperly calibrated, it consistently gives weight measurements that are either too high or too low. In research or quality control processes, identifying and correcting these errors is critical; otherwise, they will skew results and lead to incorrect conclusions. Regular calibration of equipment and implementation of rigorous testing protocols are essential strategies to minimize systematic error.
Random Errors: Challenges and Solutions
Random errors, while often unavoidable, can be mitigated through careful study design and data collection techniques. For instance, conducting repeated measurements of the same subject can help average out random fluctuations and provide a more accurate estimate. Applying statistical methods, such as using the **mean and standard deviation**, assists in quantifying the variance and reliability of your results. By recognizing the potential impact of random errors, you’re better equipped to improve data integrity.
Methods for Calculating Error
Once you understand the types of errors, the next step is selecting appropriate **error calculation methods**. Various approaches exist, each suited for different scenarios and types of data. Here we will discuss a few widely-used methods to ensure accuracy in error assessment.
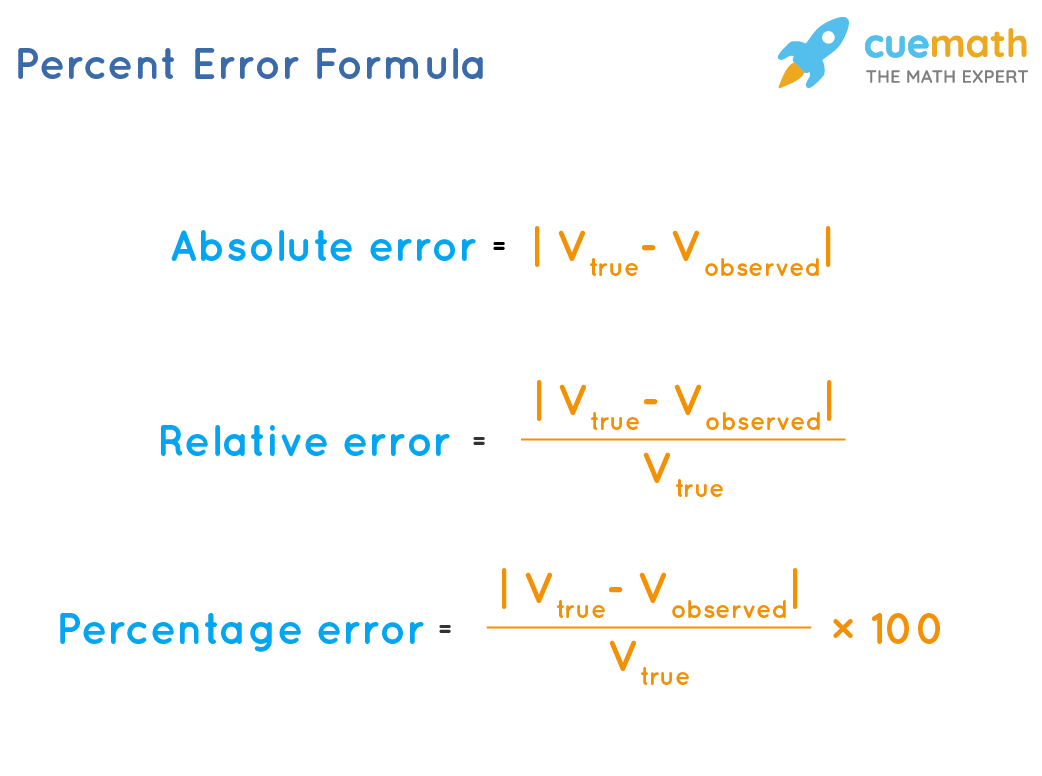
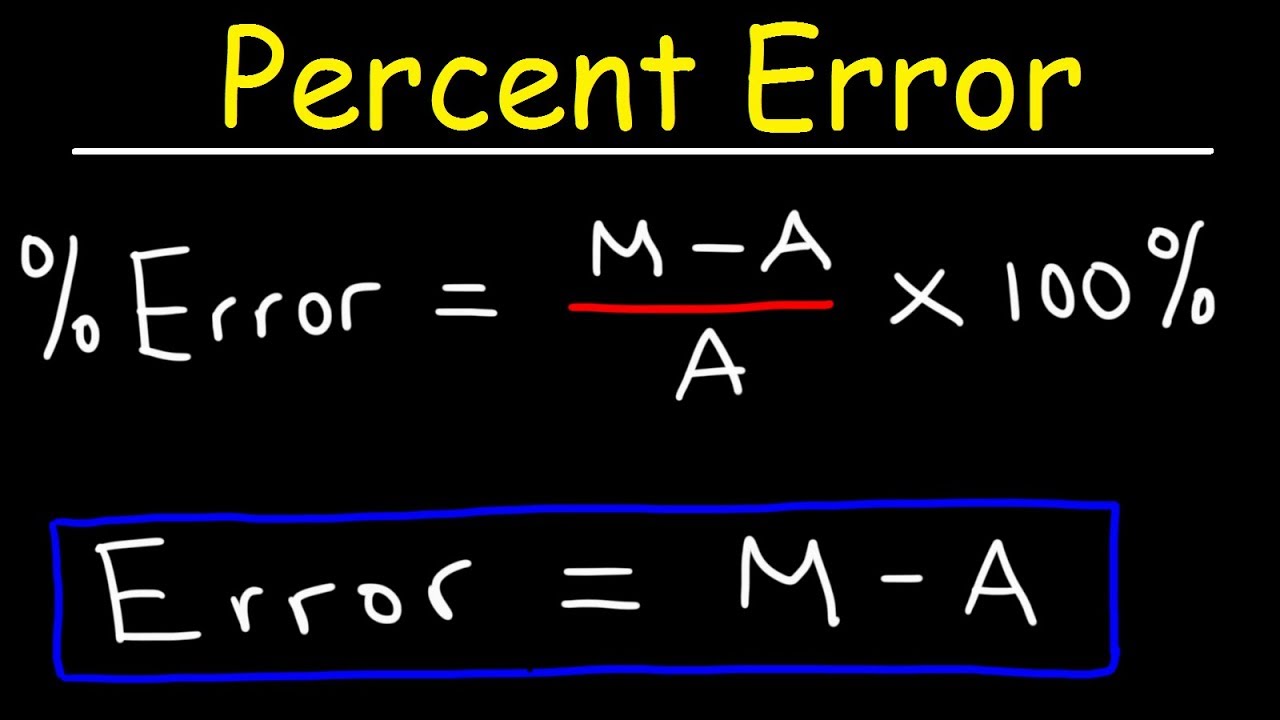
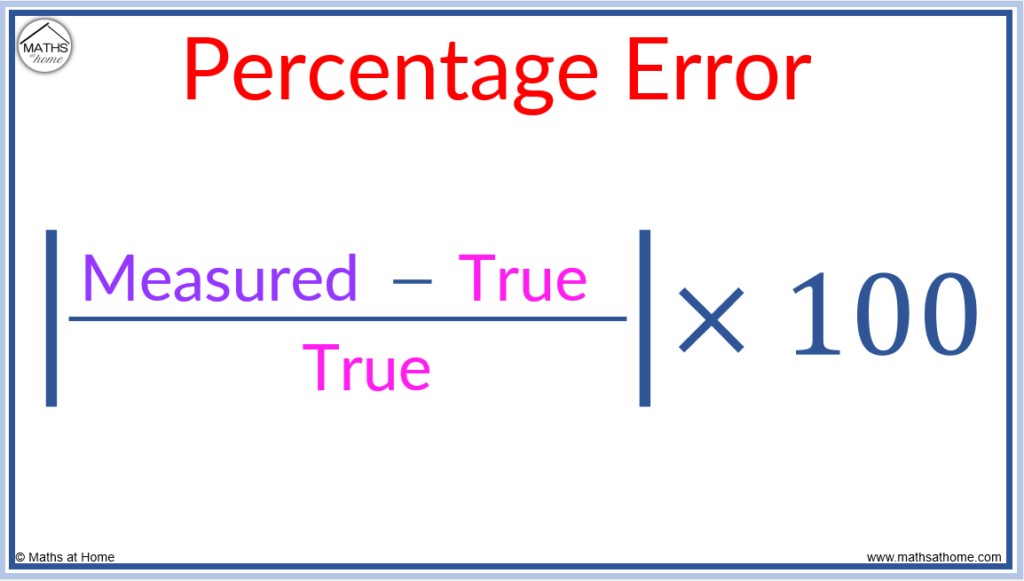
The Absolute Error Calculation
Absolute error is a straightforward method of calculating error by simply taking the absolute difference between the measured value and the true value. It’s expressed as:
Absolute Error = |Measured Value – True Value|
This method is highly effective for sensitivity analysis in various experiments. For instance, if you measure a length as 10.5 cm when the actual length is 10.0 cm, the absolute error would be 0.5 cm. This straightforward calculation helps quantify deviations effectively.
Relative Error: Understanding its Importance
While absolute error provides a straightforward metric, calculating **relative error** gives more context to the error size, especially in proportional analyses. Relative error is calculated as a ratio of the absolute error to the true value, often expressed as a percentage:
Relative Error = (Absolute Error / True Value) x 100%
This metric is particularly beneficial when comparing measurements on different scales or units. As an example, if the true value is 20 and the absolute error is 2, the relative error would be 10%. This kind of analysis helps in interpreting the significance of the error relative to the size of what’s measured.
Practical Applications of Error Calculation
Having discussed methods for error calculation, it’s crucial to explore how these methods can be practically applied across various fields to enhance accuracy in findings and conclusions.
Application in Scientific Research
In scientific research, accurately calculating error is paramount to validating hypotheses and findings. For instance, if a researcher measures the effect of a drug with error margins clearly labeled, it can provide confidence to stakeholders regarding the validity of results. Accurate error assessment can also influence public health policy and clinical guidelines, emphasizing the importance of rigorous measurement and calculation practices.
Utilization in Financial Analysis
In finance, the **calculation of error** can be vital for assessing investment risks and returns. Analysts often evaluate historical performance versus projected outcomes, using error calculations to provide insights into forecasting precision. Understanding the error margins can drastically improve the decision-making process regarding investment opportunities and risk assessments.
Conclusion
Accurately calculating error is fundamental for success in 2025 across various domains, including science, engineering, and finance. By understanding the types of errors, applying correct calculation methods, and utilizing error assessments in practical applications, you enhance the reliability of your work and improve decision-making processes. Moving forward, ensuring rigorous methodologies and consistent error evaluation will be essential for advancing innovative solutions.
FAQ
1. What is the difference between absolute and relative error?
Absolute error indicates the straightforward difference between a measured value and the true value, while relative error provides context to that difference in relation to the size of the measurement itself. Understanding both metrics is crucial for interpreting measurement accuracy.
2. How can systematic errors be minimized in experiments?
Systematic errors can be minimized through proper equipment calibration, standardizing procedures, and conducting double-checks on measurements. Maintaining consistency in methodologies ensures that bias is reduced, leading to more reliable results.
3. Why is it important to understand error in financial analysis?
Understanding error in financial analysis helps quantify the risk associated with investment decisions. It allows analysts to better assess historical performance against projected outcomes, providing a clearer view of potential risks and returns.
4. What are common sources of random error in data collection?
Random errors can arise from various sources, including environmental conditions, human inconsistencies, and variations in measurement techniques. Awareness of these factors can lead to improved data collection practices and more accurate results.
5. How does error calculation affect public health policies?
Accurate error calculation in research studies significantly influences public health policies by determining the trustworthiness of findings reflecting medical treatments or interventions, thus shaping healthcare guidelines effectively.
For more visual references on how to calculate error, check the images below:
For further reading, please visit this resource and this additional guide.