“`html
How to Measure Density: Smart Methods for Success in 2025
Understanding how to measure density is vital across various scientific and industrial applications. With the advancement of technology in 2025, measuring density techniques have become more precise and user-friendly. This article explores essential methods for measuring density, the tools and formulas involved, and practical density measurements that can enhance your experiments and industrial processes.
Understanding Density Concepts
Before diving into density measurement methods, it’s crucial to grasp the basic concepts surrounding **density**. Density is defined as mass per unit volume (\( \text{Density} = \frac{\text{Mass}}{\text{Volume}} \)), and it varies significantly among different materials and states of matter. For accurate density measurements, one must consider not only the **density units of measurement** but also how factors such as temperature and pressure impact **density in different states of matter**. By firmly understanding density, scientists and engineers can effectively apply this knowledge in real-world density applications such as design and material selection.
Density vs Weight
One common misconception is the distinction between **density vs weight**. Weight is the force exerted by gravity on an object, while density provides insights into how compact a substance is. This understanding is essential when performing density calculations, especially when comparing materials in terms of their effectiveness or suitability for specific applications. In laboratory environments, knowing the **importance of density** allows professionals to consider both variables in their testing and development processes, ensuring informed decisions based on accurate data interpretation.
Density Measurement in Industry
In industrial applications, density measurement is fundamental to maintain quality control and optimize processes. Various **density measurement devices** such as digital density meters and traditional hydrometers play a key role in accurately assessing a substance’s density. In the food industry, for example, measuring density can help ensure consistency and safety in products, while in pharmaceuticals, **density testing techniques** are vital for ensuring that products meet stringent regulatory standards. Understanding industry-specific **density measurement** practices is essential for professionals seeking to maximize operational efficiency.
Calculating Density: Practical Approaches
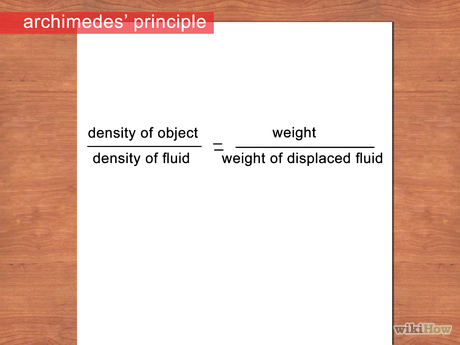
To achieve accurate density measurements, varying methods can be utilized depending on the substance’s state—solid, liquid, or gas. **Practical density measurements** utilizing **density formulas** involve straightforward calculations using specialized equipment. For example, using a calibrated volumetric flask and a scale can help measure the density of liquids effectively. As for solids, techniques like water displacement (Archimedes principle) provide an effective means for calculating density for irregularly shaped objects. Incorporating such methods into density analysis can provide reliable results across various experiments.
Density Measurement Techniques
Choosing the right method for measuring density is crucial for obtaining precise results. Several **methods for measuring density** exist, each suited for specific substances and scenarios within scientific and industrial contexts.
Density Measurement Devices
Different tools serve distinct purposes in density measurement. **Density measurement devices** like hydrometers and digital densitometers cater to various sectors from laboratory settings to fieldwork. For example, **digital density meters** allow real-time density monitoring, considerably improving the efficiency of measurement tasks. Choosing the appropriate device hinges on factors such as target precision, size of sample being measured, and the specific context of the measurement, be it in material science or fluid dynamics.
Fluid Density Measurement Methods
Measuring **fluid density** is crucial in fields such as meteorology and environmental studies. Traditional methods like using a **hydrometer** measure the pressure exerted by the fluid, which correlates with density. Advanced techniques, including the use of **machine learning in density measurement**, can enhance prediction accuracy, particularly when working with varying temperature or chemical compositions. Understanding these fluid density measurement methods is essential for researchers tasked with studying chemical processes or environmental science.
Density in Gases and Solids
The measurement of **density in gases** presents unique challenges primarily due to their compressible nature. Techniques such as using **density formulas** in combination with gas volume and temperature data enhance accuracy. Conversely, **density in solids** generally utilizes simple mass-to-volume ratios, with additional considerations for external factors such as pressure and thermal expansion. As scientific studies advance, approaches for accurately determining density in both gases and solids will continue to evolve.
Density Analysis Tools and Calculation Examples
Tools for **density analysis** form the backbone of research and industrial practices aiming for precision and accuracy. Utilizing software and analytical approaches optimally allows for effective calculations and predictions.
Density Conversion Charts
**Density conversion charts** are integral for converting values between various units and must be a part of your measuring toolkit. When conducting **density calculations**, utilizing these charts ensures that one adheres to standard measurement practices, further enforcing compliance and consistency. This is especially important when communicating findings across international borders with differing unit practices.
Specific Gravity and Its Importance
**Measuring specific gravity** is closely related to density but focuses on comparing the density of a substance to that of a referential medium, typically water. This measurement is key in numerous applications, from quality control in manufacturing to data categorization in environmental studies. Learning how to accurately perform this measurement can enhance one’s capability in various scientific regimes.
Common Density Mistakes to Avoid
Identifying and avoiding common mistakes in density measurement is essential for reliable results. Examples include neglecting temperature effects on density and incorrectly interpreting liquid level readings. A structured methodology that emphasizes accuracy and consistency helps mitigate such errors, aiding researchers and professionals alike.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the fundamental concept of density is vital for accurate measurement.
- Choose appropriate measuring devices for practical density assessments.
- Thoroughly comprehend density measurement methods suited for different states of matter.
- Incorporate structured analysis tools to improve density calculation accuracy.
- Always be aware of common pitfalls in density measurements to ensure reliability.
FAQ
1. What is the significance of density in scientific research?
The significance of **density in science experiments** lies in its ability to provide essential information regarding material properties, phase behavior, and chemical dynamics. Accurate density measurements contribute to a deeper understanding of substances, enabling scientists to predict behavior under various conditions.
2. How can temperature affect density measurements?
Temperature changes can significantly affect **fluid density measurements**, leading to variations in results. Usually, as temperature increases, density decreases, especially for liquids. Thus, researchers must account for temperature conditions when calculating density to ensure accuracy in their findings.
3. What is the difference between density and specific gravity?
**Specific gravity** is a dimensionless quantity that indicates how dense a substance is compared to a referential medium, usually water. While density relates directly to mass and volume, specific gravity provides a comparative measure, essential for various practical applications, including laboratory work and environmental studies.
4. What are some typical applications of density measurements?
Density measurements are significant in industries such as pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, and petrochemical engineering. They help monitor quality, support compliance with regulations, and guide material selection processes. Understanding these applications enhances knowledge of **density’s importance in industry**.
5. How can machine learning improve density measurement accuracy?
Incorporating **machine learning in density measurement** can enhance the accuracy and speed of data analyses, allowing for more refined models and predictions. These advanced computational methods can help interpret complex datasets and optimize density measurement protocols across various scientific and industrial settings.
“`