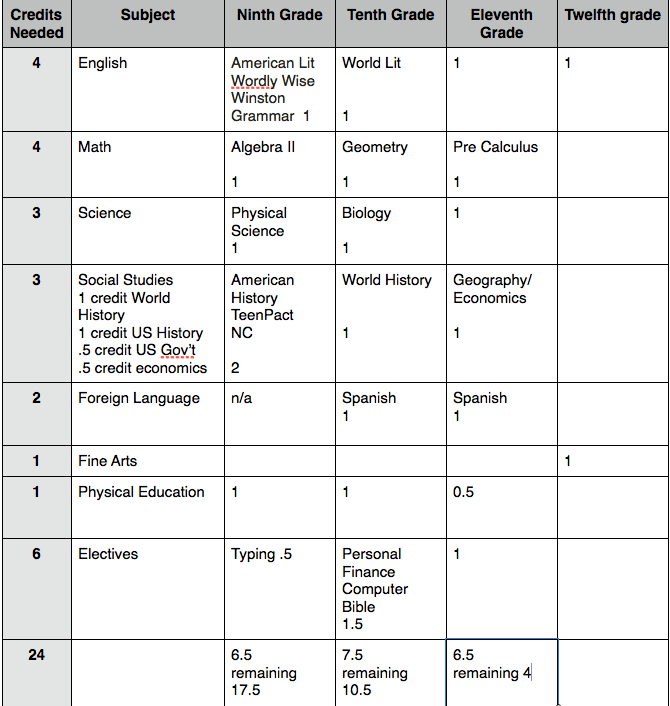
Effective Strategies for Breeding Ghazt in My Singing Monsters Breeding Ghazt, one of the most iconic monsters in My Singing Monsters, can be a challenging yet rewarding experience. The 2025 guides are essential for players seeking to enhance their monster collection and perfect their breeding techniques. This article delves into proven tips and strategies to boost your efficiency in breeding Ghazt,...
```html Smart Ways to Remove Permanent Marker Effortlessly in 2025 Permanent markers can create significant challenges when it comes to cleaning. Whether your child accidentally drew on the wall or you spilled ink on your favorite shirt, knowing how to remove permanent marker is essential. In this article, we’ll explore various methods to remove permanent marker from different surfaces including skin, fabric,...
Effective Ways to Tame a Horse in Minecraft: A Comprehensive Guide Taming a horse in Minecraft is not just a fun endeavor; it enhances your gameplay experience significantly. Horses in Minecraft offer various benefits, including faster travel and companionship during your adventures. They enable exploration and improve your efficiency in the game, making understanding the taming mechanics crucial. This guide aims...
Smart Ways to Frame a Wall in 2025: Step-by-Step Guide Framing a wall is a critical skill for any DIY enthusiast or professional carpenter. As we progress into 2025, understanding the latest wall framing techniques and technologies can greatly enhance the construction, insulation, and overall integrity of a wall. This guide will not only cover the fundamentals of how to frame...
Simple Ways to Find Blocked Numbers on iPhone Understanding Blocked Numbers on Your iPhone If you’ve ever found yourself wondering how to find blocked numbers on your iPhone, you’re not alone. Many iPhone users experience confusion regarding how to manage their blocked contacts effectively. Blocking can be a useful feature to avoid unwanted calls and messages, but it can also leave you...
How to Properly Draw a Ghost: 5 Easy Steps for Beginners Drawing ghosts can be a fun and creative endeavor, perfect for beginners and experienced artists alike. These eerie yet charming figures have captivated imaginations in art for centuries. Whether you're preparing for a Halloween project, looking to enhance your drawing skills, or simply expressing your artistic side, knowing how to...
Effective Ways to Determine Net Force in Physics To understand motion in physics, comprehending the concept of net force is essential. The net force is the total force resulting from the vector addition of all individual forces acting on an object. This metric not only helps predict how an object will move but plays a pivotal role in many practical applications...
Smart Ways to Get Shorter: Practical Tips for 2025 The quest for a healthier lifestyle often challenges individuals to rethink their habits and lifestyle choices. As we enter 2025, the focus on achieving a balanced and effective approach to health becomes even more crucial. In this article, we will explore practical strategies that can help you feel lighter and more energized...
Best 5 Ways to Properly Clean Grapes in 2025 Understanding the Importance of Cleaning Grapes Cleaning grapes might seem like a small step in food preparation, but it is crucial for ensuring the safety and healthiness of the fruit you consume. With pesticide residues and dirt being common contaminants, knowing how to clean grapes effectively is essential. Proper washing can help you...
Effective Ways to Clean Your Mouse Pad in 2025: Keep It Fresh In our tech-driven world, maintaining a clean workspace is vital not just for aesthetics but also for hygiene and productivity. One often-overlooked item that plays a critical role in this equation is the mouse pad. Over time, these small surfaces can accumulate dirt, sweat, and bacteria, significantly compromising their...